Sin x sin y = 2 sin( (x y)/2 ) cos( (x y)/2 ) cos x cos y = 2 sin( (xy)/2 ) sin( (x y)/2 ) Trig Table of Common Angles;Find dy/dx sin (xy)=x^2y sin(xy) = x2 − y sin ( x y) = x 2 y Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (sin(xy)) = d dx (x2 − y) d d x ( sin ( x y)) = d d x ( x 2 y) Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more stepsIf u=sin1((x^2y^2)/(xy)) then show that x(du/dx)y(du/dy)=tan u MATHEMATICS1 question answer collection
Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 1 349 3 2f1 Pdf
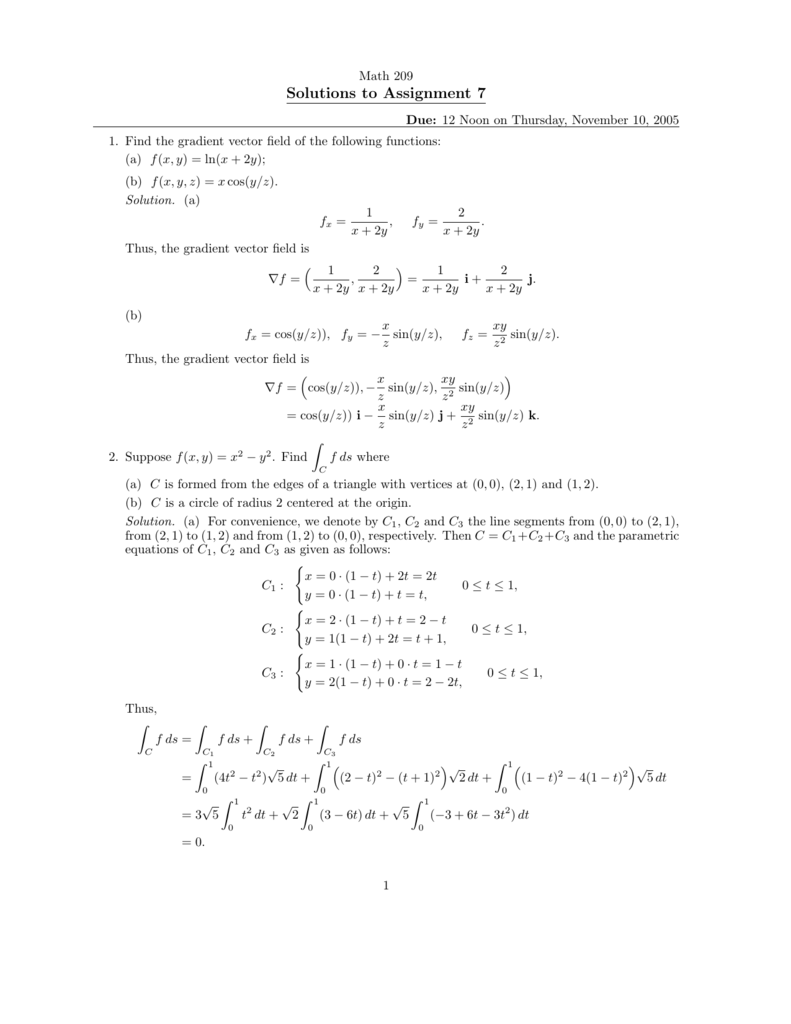
F(x y)=(x^2+y^2)sin(1/(x^2+y^2))
F(x y)=(x^2+y^2)sin(1/(x^2+y^2))-Y * sin(x)dx (two cos(x))dy= zero ;Ii) f(x,y) = x2 y2, D recinto limitado por y = x2, x = 2, y = 1 iii) f(x,y) = x 2y, D es el primer cuadrante del c´ırculo x y2 ≤ 4 iv) f(x,y) = y, D = {(x,y) y > 0, x2 y2 ≤ a2, y2 ≥ 2ax, x ≥ 0} Solucion´ i) Los puntos de interseccion de las curvas y = senx, y = 2x/π son (0,0) y (π/2,1) La integral se calcula entonces de
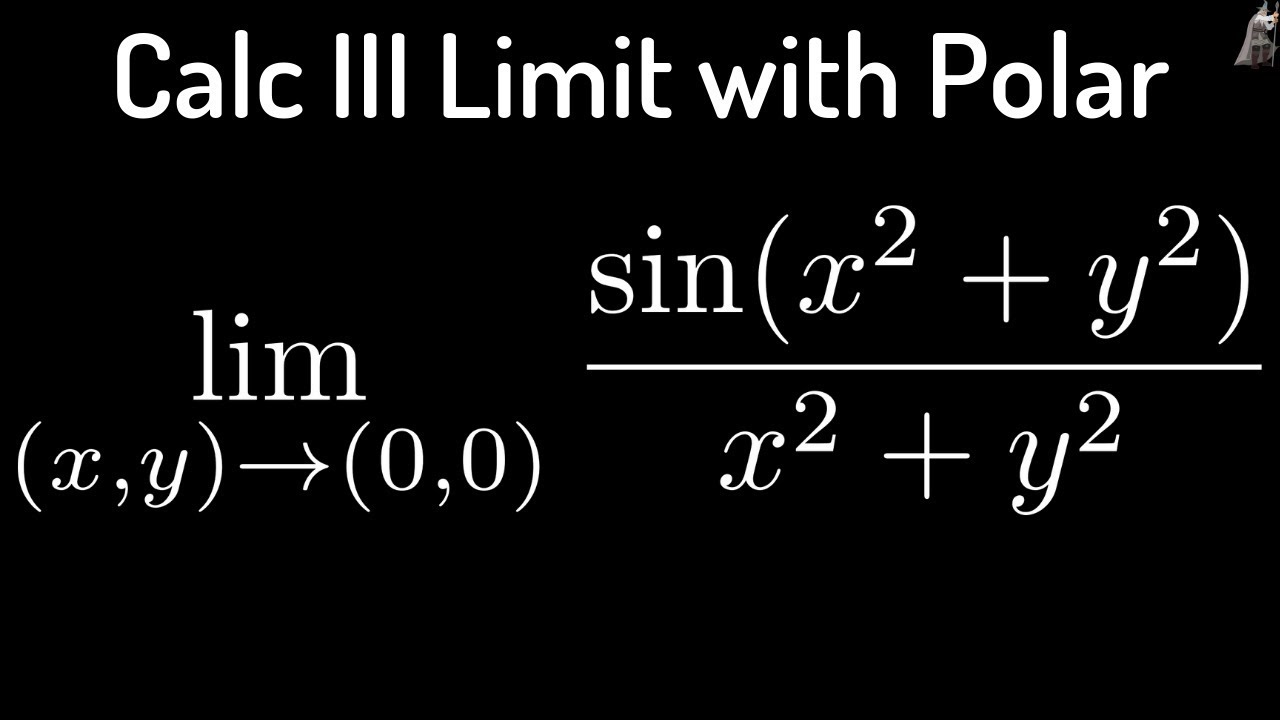



Limit Of Sin X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Using Polar Coordinates And L Hopital S Rule Youtube
Misc 3 Prove that (cos x cos y)2 (sin x – sin y)2 = 4 cos2 (x y)/2 Taking LHS (cos x cos y )2 (sin x – sin y )2 = ("2cos (" (𝑥 𝑦)/2 ") cos (" (𝑥 − 𝑦)/2 ")" )^2 ("2 cos (" (𝑥 𝑦)/2 ") sin (" (𝑥 − 𝑦)/2 ")" )^2 = ("22 cos2 (" (𝑥 𝑦)/2 ") cos2 (" (𝑥 − 𝑦)/2 ")" ) ("22 cos2 (" (𝑥 𝑦)/2 ") sin2 (" (𝑥 − 𝑦)/2If, cos^4x/cos^2y sin^4x/ sin^2y = 1 then show that cos^4y/cos^2x sin^4y/ sin^2x = 1 Maths Introduction to TrigonometryY''=sin(x)/cos^3(x) y' = sinxcosx;
A is opposite to A, b oppositite B, cSinx siny= 2sin x y 2 cos xy 2 cosx cosy= 2cos xy 2 cos x y 2 cosx cosy= 2sin xy 2 sin x y 2 The Law of Sines sinA a = sinB b = sinC c Suppose you are given two sides, a;band the angle Aopposite the side A The height of the triangle is h= bsinA Then 1If aWhere M and N are functions of x and y Calculation M = α xy 3 y cos x N = x 2 y 2 β sin x \(\frac{{\partial M}}{{\partial y}} = 3\;\alpha \;x{y^2} \cos x\) \(\frac{{\partial N}}{{\partial x}} = 2x{y^2} \beta \cos x\) The differential equation to be exact, 3 α xy 2 cos x = 2xy 2 β cos x \( \Rightarrow 3\alpha = 2 \Rightarrow \alpha = \frac{2}{3}\)
Angle 0 30 45 60 90;1 cos2 x, jcosxj= p 1 sin2 x jsinxj= tanx p 1 tan2 x, jcosxj= 1 p 1 tan2 x Formule di addizione Formule di prostaferesi sin(x y) = sinxcosy cosxsiny sinx siny= 2sin x y 2 cos x y 2 sin(x y) = sinxcosy cosxsiny sinx siny= 2sin x y 2 cos x y 2 cos(x y) = cosxcosy sinxsiny cosx cosy= 2cos x y 2 cos x y 2 cos(x y) = cosxcosy sinxsiny(類題12-1の解答) (1) y = −log(C −ex) (2) y = Ce12x 2 (3) x2 y2 = C (4) y = log(ex C) (5) y =0;



If 2 Sinx Dydx Y 1 Cos X 0 And Y 0 1 Then Y Pi 2 Is Equal To




Drawing The 3d Curve Z Xy Sin X 2 Y 2 With Tikz Tex Latex Stack Exchange
Move right part of the equation to left part with negative sign The equation is transformed from $$x^{2} y^{2} = 36$$ to $$\left(x^{2} y^{2}\right) 36 = 0$$Solution Let f(x,y,z) = x2 2y2 3z2The normal vector of the plane 3x − 2y 3z = 1 is h3,−2,3i The normal vector for tangent plane at the point (xWe have to prove the identity sin x sin y = 2*sin((x y)/2)*cos((x y)/2) Start with 2*sin((x y)/2)*cos((x y)/2), use the rules sin(A B) = sin A*cos B cos A*sin B and cos(A B) = cos



Http Edshare Soton Ac Uk Id Document 4309



Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download
Answer=0 Maximum value of a sine function is 1And if sum of 2 sine functions=2,that means both of them are individually equal to 1Hence,in this question,sin (x)=1 and sin (y)=1,which means x= (nπ/2) and y= (mπ/2)Hence,cos (x)cos (y)=cos (nπ/2)cos (mπ/2)=00=0 545 viewsSin − 1 x ) 2 , then show that ( 1Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If log√(x^2y^2) = tan^1 (yx), then prove that dydx = x yx y
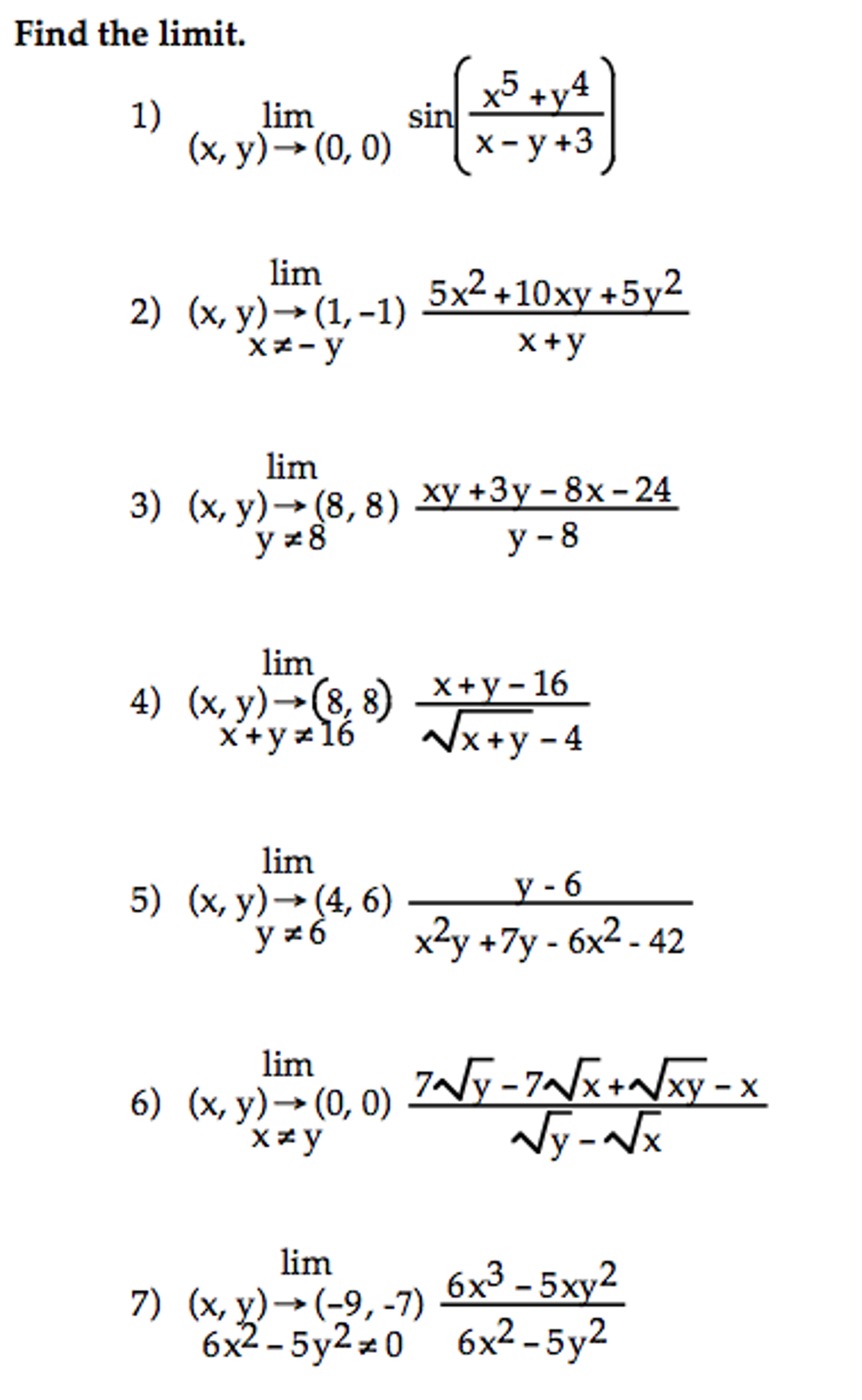



Find The Limit Lim X Y Rightarrow 0 0 Sin X 5 Chegg Com



Search 1 2 Sqrt 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 2 1 X 2 Y 2 Sin X 3 Y 5 7 1 4 From 1 6 To 1 6 On Google Computer Version And This Happens Crazyvirtualthings
Find X Y and X2 Y2 Mathematics(The notation sin 2 (x) is equivalent to (sin(x)) 2Warning sin1 (x) stands for arcsin(x) not the multiplicative inverse of sin(x)) By observing the graphs of sine and cosine, we can express the sine function in terms of cosine and vice versa = 2 * ( sin(x/2)cos(x/2) sin(y/2)cos(y/2) * ( sin^2 (x/2) cos^2 (x/2) ) Nun gibt es ja die berühmte Formel sin^2 (z) cos^2 (z) = 1, also ist der rote Faktor weg und du hast



If Y X Is A Solution Of 2 Sinx 1 Y Dy Dx Cosx And Y 0 1 Then Find The Value Of Y P 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Explaining The Graph Of Sin X 2 Sin Y 2 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Transcribed image text Find dy/dx By implicit differentiation 2x^2 xy y^2 = 2 x^3 xy^2 y^3 = 1 xe^y = x y cos(xy) = 1 sin y e^y sin x = x xy xy = Squareroot x^2 y^2 x sin y y sin x = 1 Previous question Next question Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculator Example 39 If y = A sin x B cos x, prove d2y/dx2 y = 0 Example 39 If 𝑦 = A sin𝑥B cos𝑥, then prove that 𝑑2𝑦/𝑑𝑥2 y = 0 𝑦 = A sin𝑥B cos𝑥Differentiating 𝑤𝑟𝑡𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = 𝑑(A sin𝑥 B cos𝑥" " )/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = 𝑑(A sin𝑥 )/𝑑𝑥 𝑑(B cos𝑥 )/𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = A 𝑑(sin𝑥 )/𝑑𝑥 BX^2(y(x^2)^(1/3))^2 = 1 Natural Language;
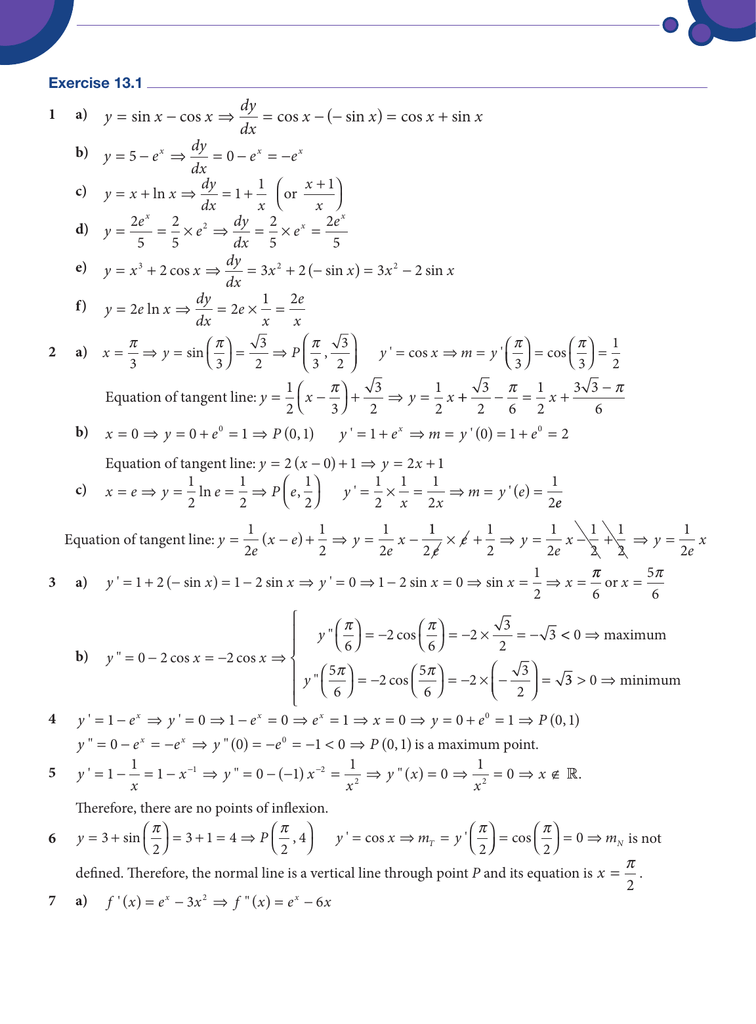



X X Dy Dx X X X X Sin Cos Cos Sin Cos Sin




Engineering Mathematics Notes
Thus, T is defined by the inequalities 0 < x < y < 2x < 1 For every (x,y) in T, xy > x2 and x2 y2 < 5x2 Show that all solutions of y'= \frac {xy1} {x^21} are of the form y=xC\sqrt {1x^2} without solving the ODE Show that all solutions of y′ = x21xy1 are of the form y = x C 1x2Y * sin(x)dx (2cos(x))dy=O1) via Wikipedia, the heart shape itself is likely based off the shape of the silphium seed, which was used as a contraceptive, or of course various naughty bits of anatomy And condom sales spike around Vday Relevancy #1 check 2) It's an equation And it



Find An Implicit Formula Satisfied By Solutions Of Y Y Ex 2y Sin X Stumbling Robot



Http Portal Unimap Edu My Portal Page Portal30 Lecture notes Imk Semester 2 sidang akademik 0910 Eqt102 Persamaan pembezaan Pdf
Mumbai University > First Year Engineering > Sem 1 > Applied Maths 1 Marks 6 M Year May 15 If cos^1 x/^2 2 xy/ab cos α y^2/b^2 = sin^2 αY multiply by sinus of (x)dx plus (two plus co sinus of e of (x))dy equally zero ;



Http People Math Umass Edu Wchen M331 Midterm Sol Pdf



Http Webpages Math Luc Edu Rgoebel1 Teachingarchive Fall11math263 Pdf Q4samplebsol Pdf
Asked 5 years, 5 months ago Active 1 year, 11 months ago Viewed 3k times 0 With f ( x, y) = ( x 2 y 2) sin ( 1 / x 2 y 2 ( x, y) ≠ 0, 0 ( x, y) = 0 Using the definition of differentiability, would I expand f ( v h) (the vector representation) to f (xh,yh), then go from there, and deduce the linear transform needed to set theBeyond simple math and grouping (like "(x2)(x4)"), there are some functions you can use as well Look below to see them all They are mostly standard functions written as you might expect You can also use "pi" and "e" as their respective constants PleaseIf X Y = 7/2 CISCE ICSE Class 9 Question Papers 10 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 6 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos 291 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all ads If X Y = 7/2 "And Xy" =5/2 ;



Cos X Cos Y 2 Sin X Sin Y 2 4sin 2 X Y 2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com J6dp2sbb




Ex 9 6 1 Find General Solution Dy Dx 2y Sin X Ex 9 6
The graph of y=sin(x) is like a wave that forever oscillates between 1 and 1, in a shape that repeats itself every 2π units Specifically, this means that the domain of sin(x) is all real numbers, and the range is 1,1 See how we find the graph of y=sin(x) using the unitcircle definition of sin(x)SOLUTION 13 Begin with x 2 xy y 2 = 1 Differentiate both sides of the equation, getting D ( x 2 xy y 2) = D ( 1 ) , 2x ( xy' (1)y) 2 y y' = 0 , so that (Now solve for y' ) xy' 2 y y' = 2x y, (Factor out y' ) y' x 2y = 2 x y, and the first derivative as a function of x and yY = sinx y = sin(x 1) y = sin(x 2) Changing c effectively shifts the graph to the left or to the right This phase shift is determined by c/b For example, when c = 1 (graphed in red), the graph has the same period and amplitude as when c = 0 (graphed in pink), but has been shifted (1/1) = 1, or 1 unit to the left When c = 2 (graphed




Graph F X Y Sin Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Study Com



Q Tbn And9gct1on0v06ru3be5zp10b5ft94umzeku7dgfp8mjl Tvanliyfl5 Usqp Cau
If x = ) 2 – (y/b) 21 y = − x2 2 C (6) y = x2 4 1!2 (7) y = Cx1 (8) y2 = C(2x− 1) (9) y =2x (10) y = e−cosx 例題12-2 dy dx = y xを解きなさい (例題12-2の解答) dy dx = yの解y = Cexp(x)を用いて,y = C(x)exp(x) とおいて, C(x)に関する微分方程式をつくるConvert to polar coordiantes The region of integration is the sector of the unit circle between θ = π / 4 and θ = 3 π / 4, and 0 ≤ r ≤ 1 Therefore, the integral is ∫ π / 4 3 π / 4 ∫ 0 1 r sin ( r 2) d r d θ Now this integral can be solved easily with the substitution r 2 = u Share



Http Edshare Soton Ac Uk Id Document 5921



14 2 Limits And Continuity
The equation (x^2 y^2 2x 4y 4) k(y 7x 2) = 0 \tag1 is equivalent to x^2 y^2 (2 7k)x (4 k)y (4 2k) = 0, which is clearly the equation of a circle Moreover, if a The equation is equivalent to x 2 y 2 ( 2 − 7 k ) x ( 4 k ) y − ( 4 2 k ) =X Y x=y2 y=x2 (1,1) (4,2) Figure 2 The area between x = y2 and y = x − 2 split into two subregions If we slice the region between the two curves this way, we need to consider two different regions Where x > 1, the region's lower bound is the straight line For x < 1, however, the region's lower bound is the lower half of theY sin(x)dx (2cos(x))dy=0;



Solutions To Assignment 7




Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu
Sin 2 (a) 0/4 1/4 2/4 3/4 4/4 cos 2 (a) 4/4 3/4 2/4 1/4 0/4 tan 2 (a) 0/4 1/3 2/2 3/1 4/0 ;Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystep #int sin(x^2y^2)dr = int sin(r^2)*J(r,phi)dr = int_3^8 r sin(r^2)dr# To solve this integral, we need to use substitution We substitute #u=r^2# , so #du=2rdr# ,



Search Q Sin 2x 3d 1 Tbm Isch



Limit Of Sin X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Using Polar Coordinates And L Hopital S Rule Youtube
Y multiply by sinus of (x)dx plus (2 plus co sinus of e of (x))dy equally 0;Given Triangle abc, with angles A,B,C;Graph y=sin (x/2) y = sin( x 2) y = sin ( x 2) Use the form asin(bx−c) d a sin ( b x c) d to find the variables used to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift a = 1 a = 1 b = 1 2 b = 1 2 c = 0 c = 0 d = 0 d = 0 Find the amplitude a a Amplitude 1 1
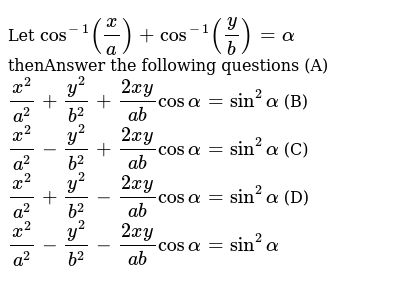



That The Function U E 2xy Sin X 2 Y 2 Is Harmonic




Engineering Mathematics Notes
`sin^(1)xsin^(1)y=cos^(1)""{sqrt((1x^(2))(1y^(2)))xy}`Welcome to Doubtnut Doubtnut is World's Biggest Platform for Video Solutions of Physics, Chemis If y = sin^1 x/√(1 x^2), then show that (1 x^2)d^2y/dx^2 3xdy/dx y = 0Ejercicios EDO's de primer orden 3 1 y3 dy = dx x2 Z y−3 dy = Z x−2 dx, 1 −2 y−2 = −x−1 c 1, −1 2y2 −1 x c 1, 1 y2 2 x c, c = −2c 1 Solución implícita 1 y2 2xc x Solución explícita y = ±



Http Www Math Ntu Edu Tw Cheng Teaching Calculus Ch15 Pdf




What Is The General Solution Of Xy 2y Sin X Mathematics Stack Exchange
Answer to \2 – } (2 x2y3 – y sin x)dA D = {(x,y) x y < Who are the experts?Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicSOLUTION 12 Begin with x 2 y y 4 = 4 2x Now differentiate both sides of the original equation, getting D ( x 2 y y 4) = D ( 4 2x) , D ( x 2 y) D (y 4) = D ( 4 ) D ( 2x) , ( x 2 y' (2x) y) 4 y 3 y' = 0 2 , so that (Now solve for y' ) x 2 y' 4 y 3 y' = 2 2x y, (Factor out y' ) y' x 2 4 y 3 = 2 2x y, and (Equation
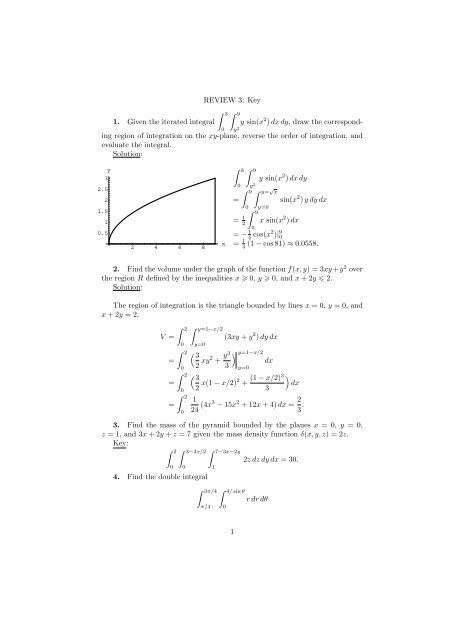



Review 3 Key 1 Given The Iterated Integral Aˆ 0 Aˆ 9 Y Sin



How To Find Dy Dx When Y Sin X 2 Y 2 Quora
Explanation sin(x y)sin(x − y) = (sinxcosy cosxsiny)(sinxcosy − cosxsiny) = sin2xcos2y −cos2xsin2y = sin2x(1 − sin2y) − (1 − sin2x)sin2y = sin2x −sin2xsin2y − sin2y sin2xsin2y = sin2x − sin2xsin2y −sin2y sin2xsin2y = sin2x −sin2y Answer linkExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject areaExtended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music




Surface Representing The Function F X Y Sin X Cos Y 1 0 X Download Scientific Diagram



Differentiate Y Sin X 2 X Sin Y 2 Math Central
162 Line Integrals We have so far integrated "over'' intervals, areas, and volumes with single, double, and triple integrals We now investigate integration over or "along'' a curve—"line integrals'' are really "curve integrals'' As with other integrals, a geometric example may be easiest to understand Consider the function f = x y andX^2 2 y^2 = 1 Natural Language;



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 1 349 3 2f1 Pdf
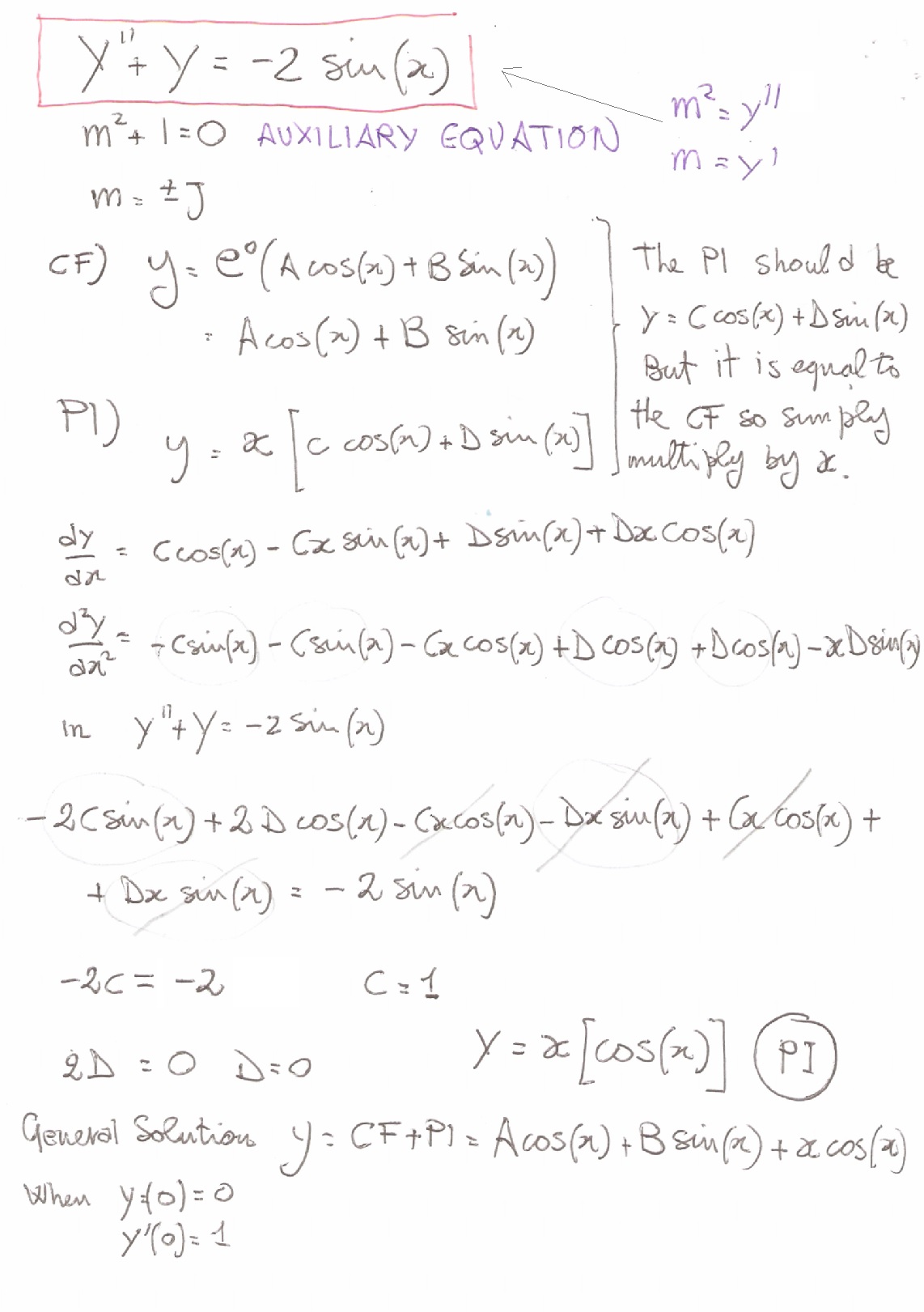



How Do I Solve Y Y 2 Sin X With The Initial Conditions Y 0 0 And Y 0 1 Socratic




Solution Of The Differential Equation X 2sin 3 Y Y 2 Cos X Dx X 3cos Y Sin 2 Y 2y Sin X Dy O Is
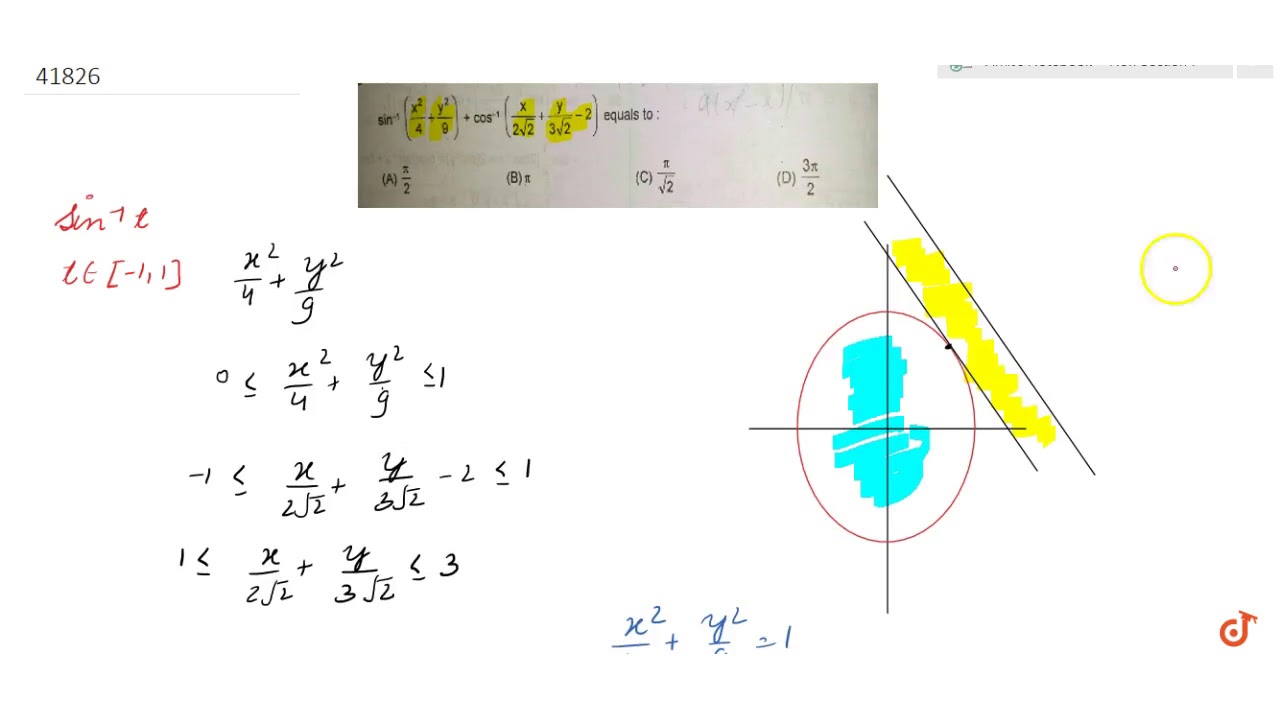



Sin 1 X 2 4 Y 2 9 Cos 1 X 2sqrt2 Y 3sqrt2 2 Youtube



Maxima 5 29 0 Manual 1 Introduction To Maxima



Is X2 Y2 Sin 1 X2 Y2 Differentiable Quora



Is X2 Y2 Sin 1 X2 Y2 Differentiable Quora
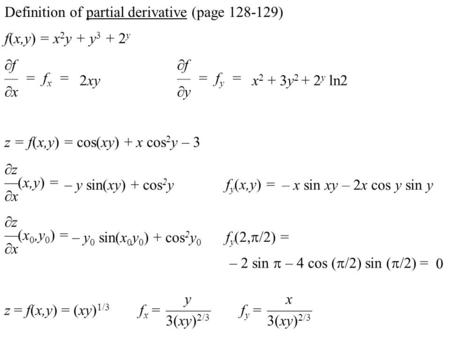



For Any Function F X Y The First Partial Derivatives Are Represented By F F Fx And Fy X Y For Example If F X Y Log X Sin Ppt Video




If Y Sin X 2 Cos X 2 2 Find Dy Dx At X Pi 6 Youtube



Document



Sigma Mathnet



Find Dy Dx When X And Y Are Connected By The Relation Sin Xy X Y X2 Y Studyrankersonline



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 1 349 3 2f1 Pdf



If Y X Is A Solution Of 2 Sinx 1 Y Dy Dx Cosx And Y 0 1 Then Find The Value Of Y P 2 Studyrankersonline



1




Consider The Following Double Integral Chegg Com




Why Is The Graph Of The Implicit Relation Sin X 2 Y 2 Cos Xy So Cool Mathematics Stack Exchange




If Y Cos Sinx 2 Then At X Sqrt Pi 2 Dy Dx Youtube
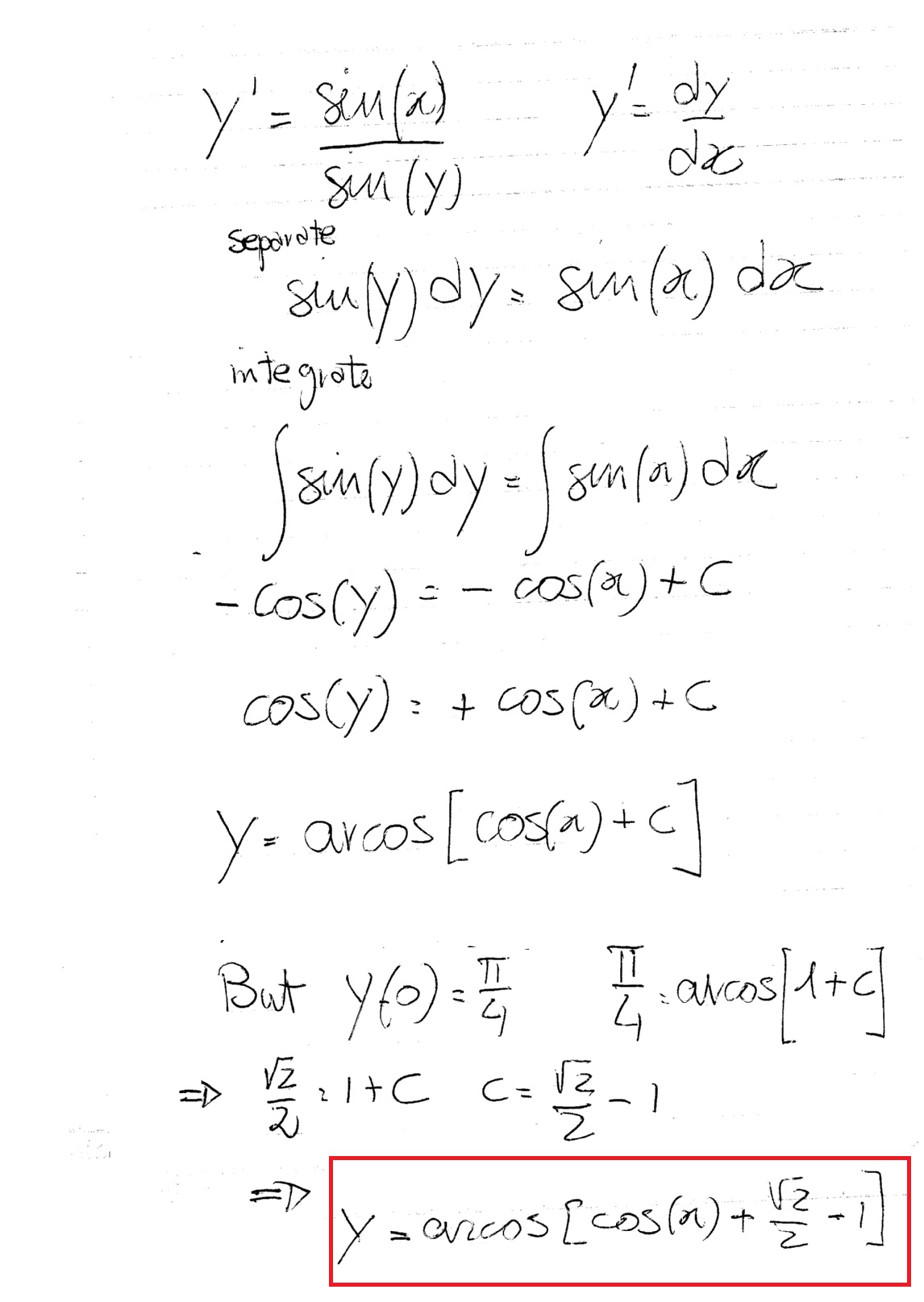



How Do You Solve The Initial Value Problem Y Sinx Siny Where Y 0 P 4 Socratic



Http Homepages Se Edu Kfrinkle Files 14 06 Math3213spring07homework2solutions Pdf



Link Springer Com Content Pdf m 3a978 1 349 3 2f1 Pdf
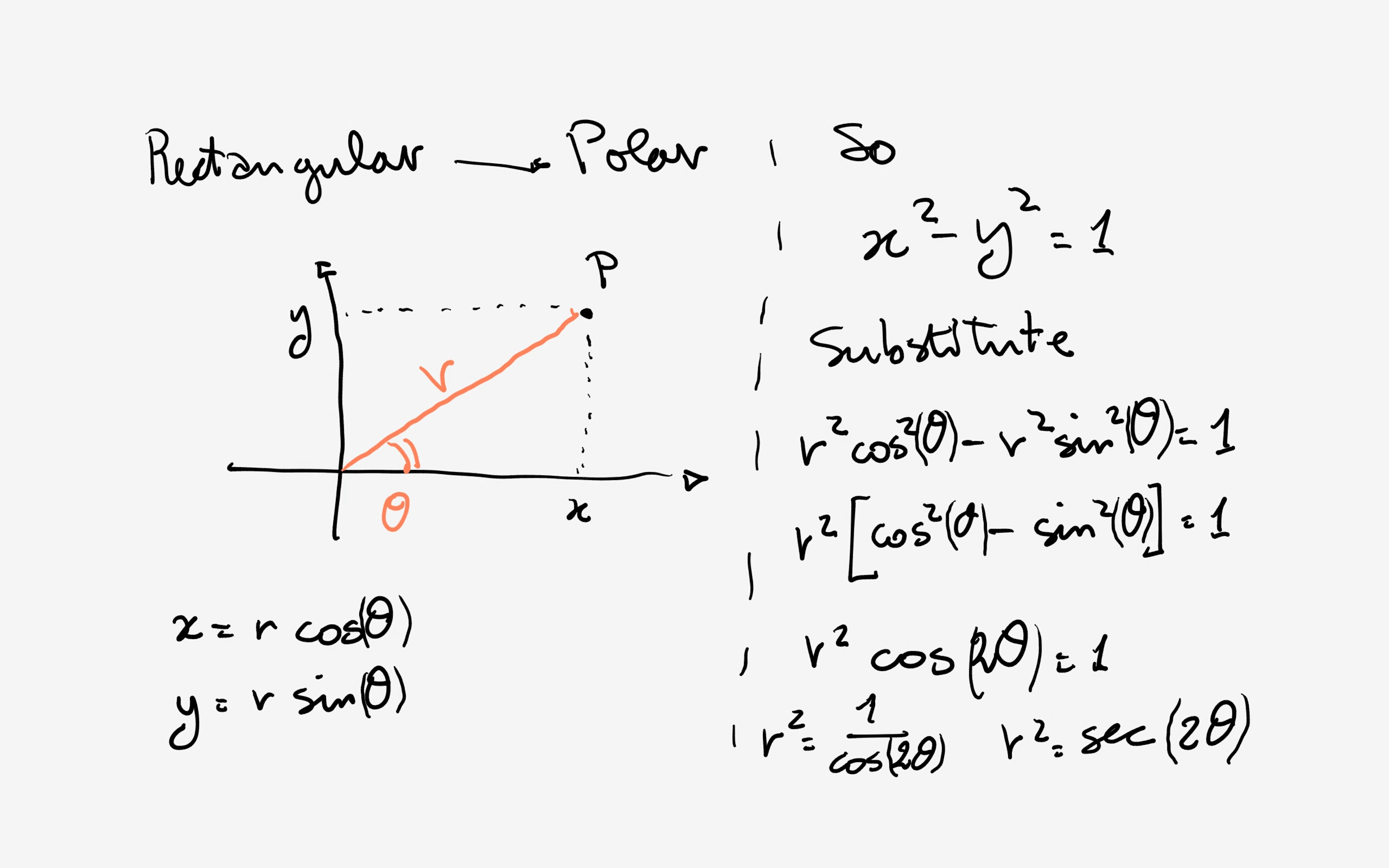



How Do You Write The Rectangular Equation X 2 Y 2 1 In Polar Form Socratic



How To Integrate Y 2 X 2 X 2 Y 2 2 Dy Quora



Manuel Barrera Y 1 X X2 Y2 9 Y 2x X 3 Sin Y




2 1 Plot Of Circle X 2 Y 2 1 And The Definitions Of Cos 8 And Sin Download Scientific Diagram




If Y Ex Sin X Prove That D2y Dx2 2 Dy Dx 2y 0 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com 5p09j033




If Sin 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Loga Then Dy Dx Is Equal To A X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 B Y X C X Y D None Of These




Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu
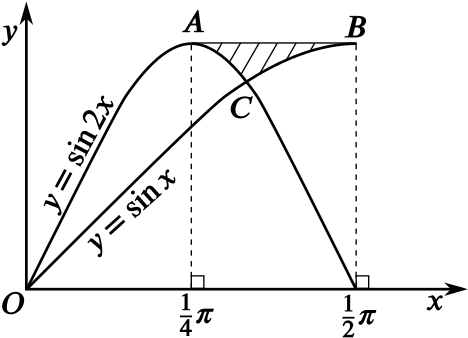



Where Do The Curves Y Sin 2x And Y Sin X Cross Calculus Of Trigonometry Logarithms Underground Mathematics



Wykresy




4 A Let Sin X Cos Dr X Cos X Y 2 Dy Homeworklib




Misc 4 Prove Cos X Cos Y 2 Sin X Sin Y 2 Chapter 3




Use Polar Coordinates To Evaluate The Double Integral Chegg Com



3 10 Periodic Functions Theoretical Physics Reference 0 5 Documentation



Find Limit Of A X Y Function Lim X Y Tends To Chegg Com




Ppt Drill Find Dy Dx Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



1



Http Www Math Mtu Edu Ipinelis Teaching Ma3160 14fall Review3 Key Pdf




If Sin X Sin Y 3 4 And Sin X Sin Y 2 5 Prove That 8 Tan X Y 2 15 Tan X Y 2 Brainly In



Answered Find X Y 4 V2r Y 2 18 Lim X Bartleby



Using The Method Of Variation Of Parameters Solve D 2y Dx 2 Y 1 1 Sinx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Graph Of Y 1 Sin X And Y 2 X 3p Fig 6 Shows The Solutions Of Download Scientific Diagram




Find The Equation Of The Tangent To The Curve Y 2 Sin X Sin 2x At X P 3 Brainly In



Surface Integrals



Www Wssd K12 Pa Us Downloads Calc mid Term review packet solutions Pdf



How Do You Draw The Graph Of Y 2 Sinx For 0 X 2pi Socratic



If Sin X Y Y X X 2 Y 2 Find Dy Dx Youtube




If Sin Xy X Y X 2 Y Find Dy Dx Brainly In



Http Www Science Marshall Edu Karna Pdfdocfiles Examsingle 229exam2 Pdf




Sketch The Graph Of Y Sin X As A Surface In Mathbb R 3 Study Com




Ex 9 6 1 Find General Solution Dy Dx 2y Sin X Ex 9 6



Www Ualberta Ca Csproat Homework Math 215 Solution 3 Pdf




A Find The Limit Lim X Y Gt 0 0 Chegg Com




Solve The Differential Equation Dy Dx 2y Tan X Sinx Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection



12 3 Partial Derivatives Mathematics Libretexts




Finding Slope Of Tangent Line To Y 2 Sin 2 4x 3 Cos 2 2x At The Point X 0 Frac 10 Pi 3 Mathematics Stack Exchange




If Sqrt 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 Y 2 A X Y Show That Dy Dx Sqrt 1 Y 2 1 X 2 Mathematics And Statistics Shaalaa Com




Solve The Following Equation Dydx Xy Y 2e X 2 2 Sin X
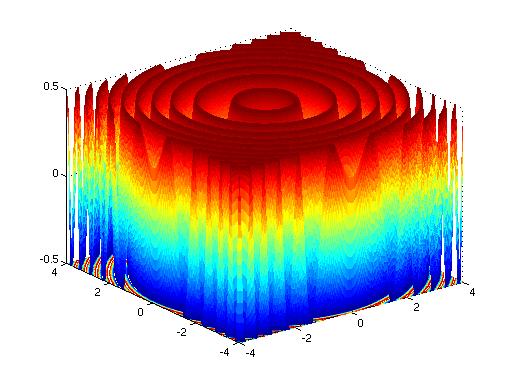



Surfacesandcontours Html




How Do You Differentiate Y Sin X 6 Tan X 2 X 2 2 2 Socratic




Graph Equations System Of Equations With Step By Step Math Problem Solver




Ex 9 2 6 Verify Y X Sin X Xy Y X Root X2 Y2




The Value Of Lim X Gty Sin 2x Sin 2y X 2 Y 2 Equals Youtube




Find D2y Dx2 Y X2 Sinx Cosx Maths Meritnation Com




If Sin X Y Y X X 2 Y 2 Find Dy Dx




Answered Practice Exercises 13 26 Implicit Bartleby



Http Www Math Montana Edu Courses M273 Reviewe3s17solutions Pdf



Www3 Nd Edu Taylor Math550 Images Currentexamsolutions Exam4f16 Pdf
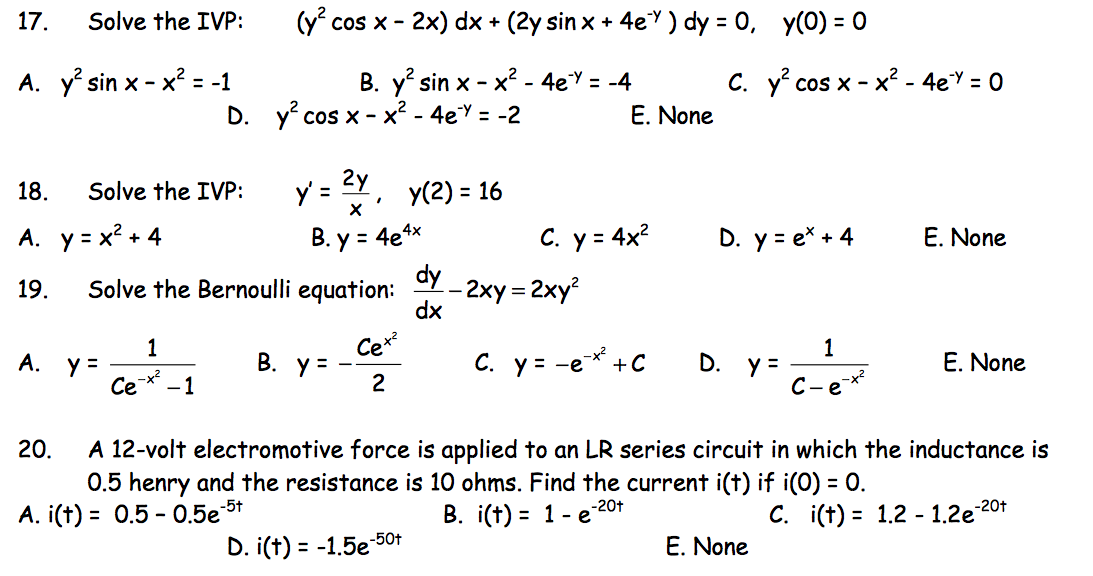



17 Solve The Ivp Cos X 2x Dx 2y Sin X 4e Y Dy 0 Chegg Com
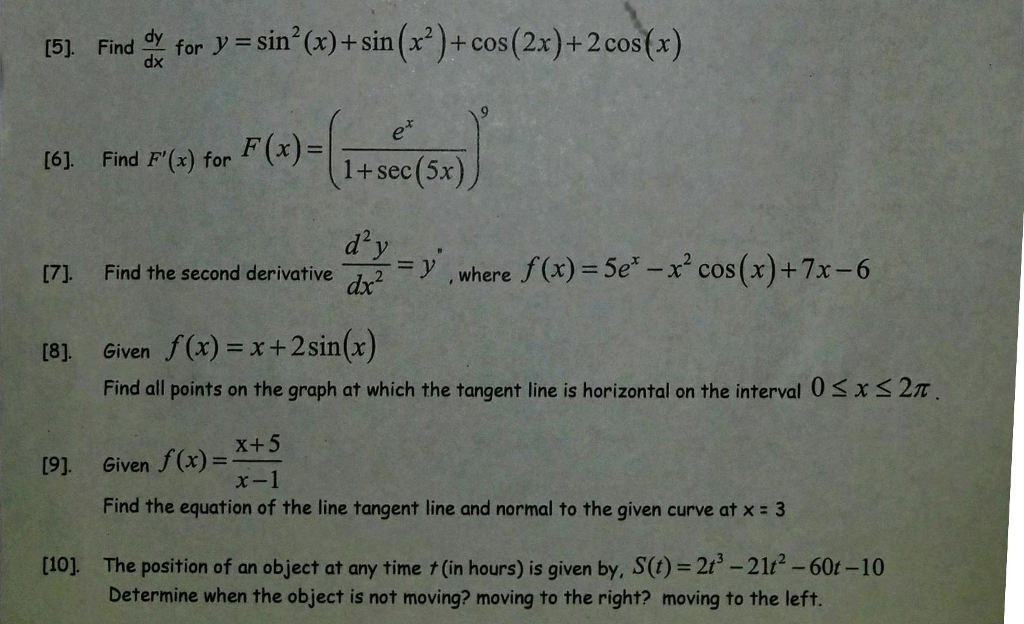



Find Dy Dx For Y Sin 2 X Sin X 2 Cos 2x Chegg Com




Solve The Differential Equation Dydx 3y Cot X Sin 2x Given Y 2 When X Pi2
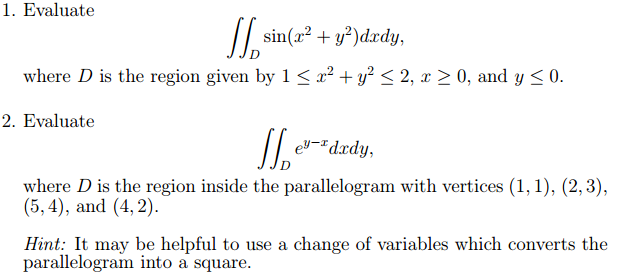



Evaluate Integral Integral D Sin X 2 Y 2 Dxdy Chegg Com



No comments:
Post a Comment